The Consumer Protection Act, 2019, is a landmark legislation in India that aims to safeguard consumer rights and address consumer grievances effectively. It replaces the Consumer Protection Act, 1986, and introduces several reforms to enhance consumer welfare and accountability among businesses. This article provides an in-depth analysis of the rights and responsibilities of consumers under the Act.
Introduction to Consumer Protection Act, 2019
The Consumer Protection Act, 2019, was enacted to address modern challenges faced by consumers in the digital age. It provides mechanisms for fast-track grievance redressal, imposes strict liability on manufacturers and sellers for defective products, and introduces new consumer rights.
Key highlights of the Act include:
- Establishment of the Central Consumer Protection Authority (CCPA)
- Stricter regulations for e-commerce platforms
- Simplified dispute resolution mechanisms
- Stringent penalties for misleading advertisements
Rights of Consumers Under the Consumer Protection Act, 2019
The Act enshrines several fundamental rights for consumers to ensure fair trade practices and protect them from exploitation.
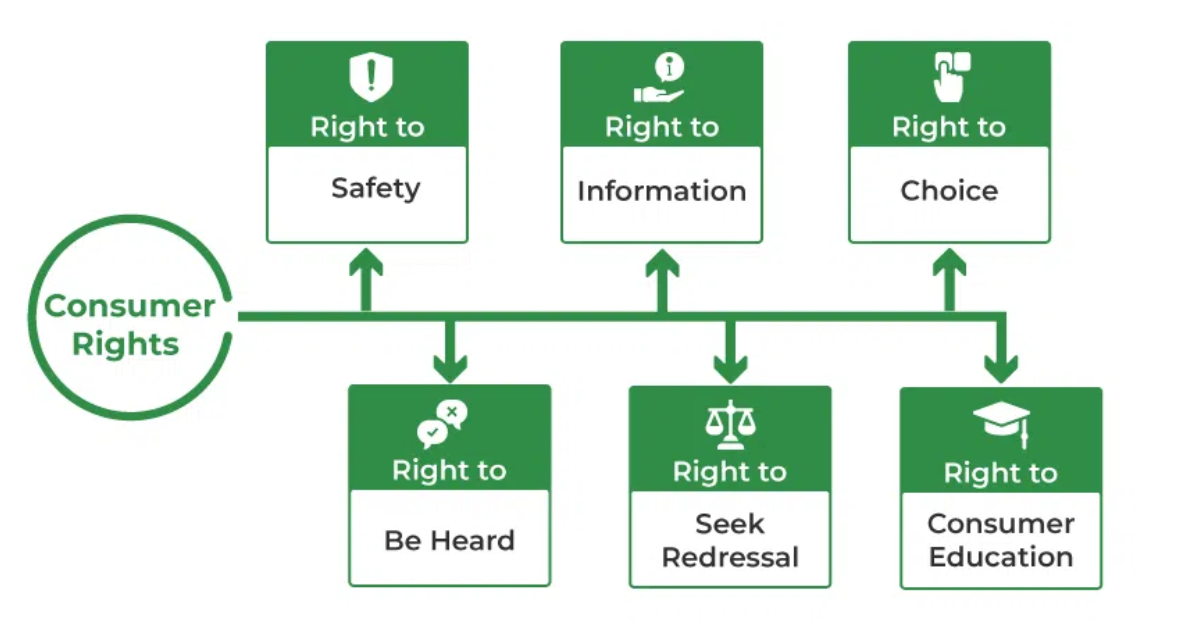
1. Right to Safety
Consumers have the right to be protected against goods and services that may be hazardous to their life, health, or property. This includes ensuring quality standards and adherence to safety norms by manufacturers.
2. Right to Information
Consumers have the right to complete and accurate information regarding the quality, quantity, potency, purity, price, and standard of products and services. Misleading advertisements and deceptive marketing practices are punishable under the Act.
3. Right to Choose
Consumers have the right to access a variety of products and services at competitive prices. They should not be coerced into purchasing a particular brand or product.
4. Right to Redressal
The Act provides consumers with the right to seek redressal against unfair trade practices, defective goods, or deficient services. The grievance redressal mechanism includes Consumer Disputes Redressal Commissions at the district, state, and national levels.
5. Right to Consumer Education
Consumers have the right to be informed about their rights and responsibilities. The government and non-governmental organizations play a role in spreading consumer awareness through campaigns and programs.
6. Right to Be Heard
Consumers have the right to voice their concerns and complaints regarding products or services. The establishment of the CCPA ensures that consumer interests are represented and protected.
Responsibilities of Consumers
While the Consumer Protection Act, 2019, grants various rights, it also emphasizes the responsibilities of consumers to ensure a fair and transparent marketplace.
1. Awareness and Vigilance
Consumers must be aware of their rights and make informed purchasing decisions. They should read labels, verify product details, and research before buying.
2. Exercising Caution While Purchasing
Consumers should check the expiry dates, price tags, and quality certifications of products before making a purchase. In digital transactions, they should ensure secure payment methods and verify seller credentials.
3. Filing Complaints When Necessary
If a consumer faces unfair treatment or receives a defective product, they should promptly file a complaint with the appropriate consumer forum.
4. Avoiding Unethical Practices
Consumers should not misuse their rights by making false complaints or engaging in fraudulent activities.
5. Environmental Responsibility
Consumers should support eco-friendly products and adopt sustainable consumption practices to reduce environmental impact.
Grievance Redressal Mechanism Under the Act
The Consumer Protection Act, 2019, introduces a three-tier grievance redressal system to resolve consumer disputes efficiently.
1. District Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission
Handles complaints where the value of goods and services does not exceed ₹1 crore.
2. State Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission
Handles complaints involving amounts between ₹1 crore and ₹10 crores.
3. National Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission
Handles complaints exceeding ₹10 crores and appeals from lower commissions.
Consumers can also file complaints online through the E-Daakhil portal, making the process more accessible.
Impact of the Act on E-Commerce
The Act introduces stringent guidelines for e-commerce platforms, ensuring greater accountability and transparency. Key regulations include:
- Mandatory disclosure of seller details
- Consumer-friendly return and refund policies
- Prohibition of false reviews and misleading advertisements
- Compliance with grievance redressal mechanisms
Conclusion
The Consumer Protection Act, 2019, is a comprehensive law that strengthens consumer rights and ensures fair trade practices in India. By being aware of their rights and responsibilities, consumers can make informed decisions, seek redressal for grievances, and contribute to a transparent marketplace.